Introduction
Administrative Law has emerged as one of the most dynamic and indispensable branches of public law in modern governance. To begin with, it regulates the powers, functions, and procedures of administrative authorities that perform executive, legislative, and quasi-judicial roles. Over time, as the functions of the State expanded beyond mere maintenance of law and order, the need for a separate legal framework became unavoidable. Consequently, Administrative Law developed to control discretion, ensure fairness, and protect individual rights.
In particular, countries like India, United Kingdom, and United States of America witnessed rapid administrative growth due to socio-economic changes. Therefore, Administrative Law today stands as a bridge between efficient administration and the rule of law. At the same time, it ensures that expanding governmental power does not become arbitrary or oppressive.
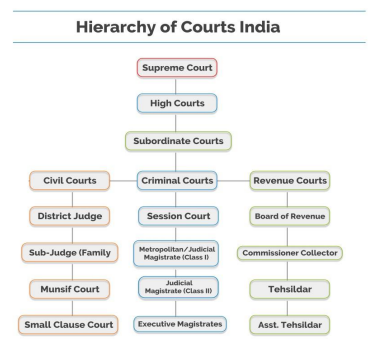
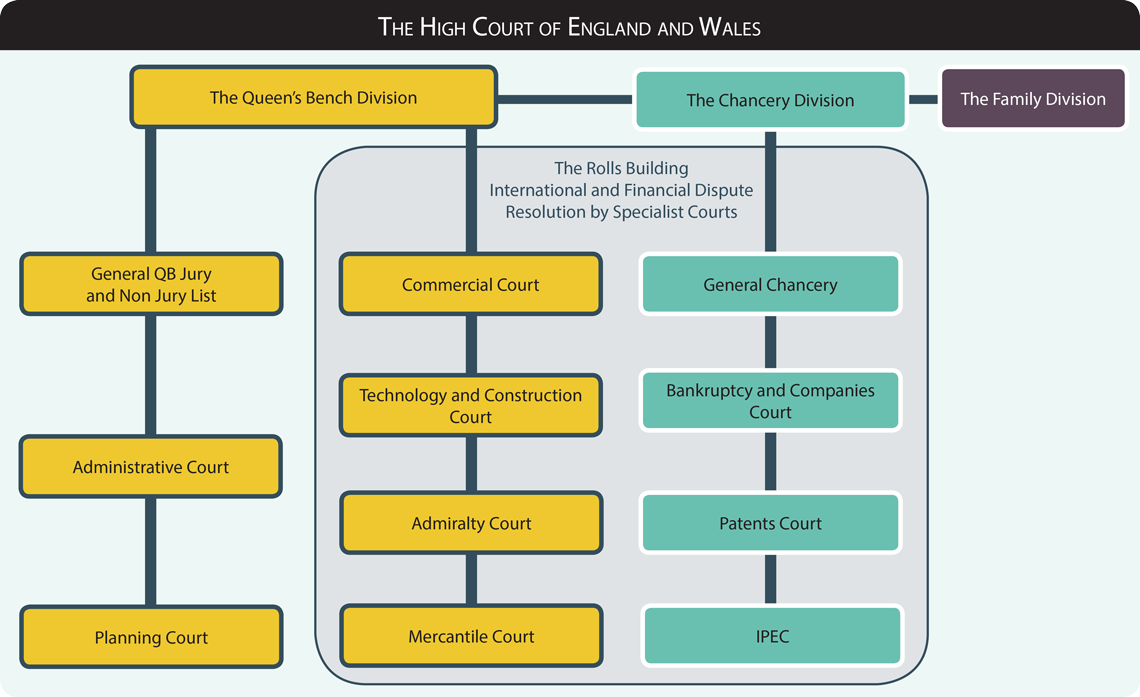

Reasons for the Growth of Administrative Law
Firstly, the rise of the welfare state is the most significant reason for the growth of Administrative Law. Modern governments actively participate in social and economic development by regulating industries, providing welfare schemes, and protecting vulnerable sections of society. As a result, administrative agencies became essential to implement these policies efficiently. Moreover, legislatures cannot foresee every practical situation, making delegated legislation unavoidable.
Secondly, the increasing complexity of governance has contributed greatly to this growth. For instance, technical fields such as environmental regulation, digital governance, taxation, and labor welfare demand expert decision-making. Hence, administrative authorities equipped with specialized knowledge became necessary. Additionally, the slow and formal procedures of ordinary courts further accelerated this trend. Therefore, tribunals and administrative bodies emerged as quicker and more flexible alternatives for dispute resolution.
Growth of Administrative Law in India
In India, Administrative Law expanded rapidly after independence due to the adoption of a written Constitution based on social justice. Notably, the State undertook large-scale responsibilities in planning, industrial development, education, health, and public employment. Consequently, numerous administrative bodies, commissions, and tribunals were created.
Furthermore, constitutional provisions such as Articles 14, 19, and 21 strengthened judicial control over administrative action. As a result, principles like natural justice, reasonableness, proportionality, and legitimate expectation became firmly established. In addition, Public Interest Litigation enabled courts to review administrative excesses. Thus, Indian Administrative Law evolved as a rights-oriented and constitutionally controlled system.
Growth of Administrative Law in the UK
Historically, the UK was hesitant to recognize Administrative Law due to its strong belief in the rule of law. However, industrialization, world wars, and welfare legislation made administrative discretion inevitable. Gradually, tribunals and inquiries became integral to governance.
Meanwhile, courts developed judicial review as a powerful mechanism to control administrative action. For example, doctrines such as ultra vires, procedural fairness, and reasonableness were used to check misuse of power. Therefore, UK Administrative Law evolved not through a written constitution but through judicial precedents and parliamentary oversight. Ultimately, efficiency and legality were balanced within a flexible legal framework.
Growth of Administrative Law in the USA
Similarly, Administrative Law in the USA developed due to economic regulation and federal governance. In particular, agencies were created to regulate trade, labor relations, consumer protection, and the environment. As a consequence, these agencies were vested with quasi-legislative, quasi-executive, and quasi-judicial powers.
At the same time, constitutional safeguards ensured that administrative power did not violate individual rights. Therefore, judicial review became a central feature of US Administrative Law. Moreover, statutory procedures and due process requirements were introduced to maintain transparency and accountability.
Classification of Administrative Law
Broadly, Administrative Law can be classified on the basis of powers, functions, and control mechanisms. Firstly, on the basis of powers, it includes rule-making, adjudicatory, and enforcement powers. Secondly, on the basis of functions, it covers administrative, quasi-judicial, and quasi-legislative actions.
Additionally, classification can be made based on control mechanisms. For instance, legislative control, executive supervision, judicial review, and public accountability act as checks on administrative authorities. Thus, each legal system adopts a suitable combination of controls. Ultimately, the objective remains to ensure efficiency without sacrificing fairness.
Comparative Perspective
Comparatively, India emphasizes constitutional supremacy and social justice. In contrast, the UK relies on parliamentary control and judicial review. Meanwhile, the USA depends heavily on statutory regulation and separation of powers. Nevertheless, all three systems share a common goal. That is, they aim to balance administrative efficiency with protection of individual rights and the rule of law.
Mnemonic to Remember the Answer
“W-CAT RULE”
W – Welfare State
C – Complexity of governance
A – Administrative agencies
T – Tribunals
R – Rule of law
U – Ultra vires control
L – Legislative & judicial oversight
E – Executive accountability
About Lawgnan
In conclusion, mastering Administrative Law is essential for law students, judiciary aspirants, and legal professionals. Therefore, if you are looking for simplified, exam-oriented, and comparative explanations of Administrative Law concepts, visit lawgana.in today. Moreover, the platform offers structured answers, mnemonics, and practical insights covering Indian, UK, and US perspectives. Whether you are preparing for university exams or competitive law entrances, lawgana.in helps you learn faster and revise smarter. So, take the next step in your legal journey and strengthen your understanding of Administrative Law with trusted, student-friendly content.




